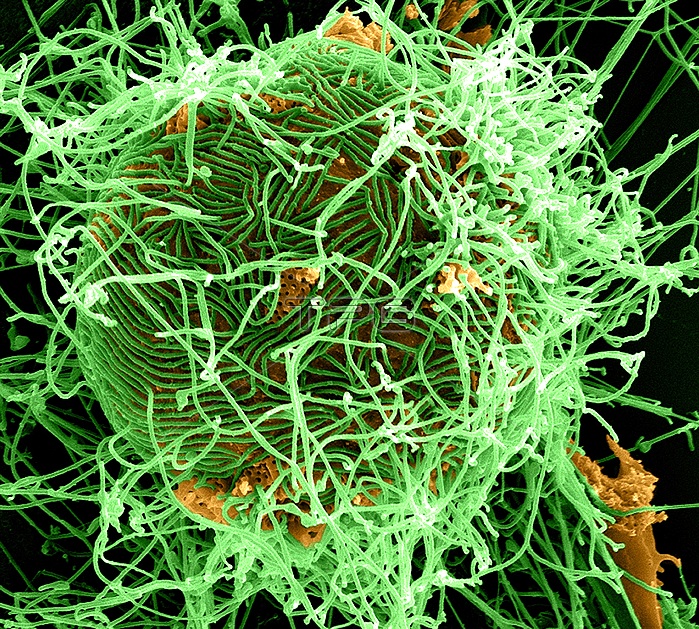
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of filamentous Ebola virus particles (green) attached and budding from a chronically infected VERO E6 cell (orange) (25,000x magnification). Produced by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), under a magnification of 25,000X, this digitally-colorized scanning electron micrograph (SEM) depicts numerous filamentous Ebola virus particles (green) budding from a chronically-infected VERO E6 cell (orange). Ebola hemorrhagic fever (Ebola HF) is one of numerous Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers. It is a severe, often fatal disease in humans and nonhuman primates (such as monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees). Ebola HF is caused by infection with a virus of the family Filoviridae, genus Ebolavirus. When infection occurs, symptoms usually begin abruptly. The first Ebolavirus species was discovered in 1976 in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo near the Ebola River. Since then, outbreaks have appeared sporadically.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP13731317
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading