
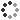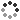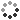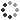
Daniell Cell. This is an electrochemical cell invented by John Daniell in 1836. It consists of a beaker containing a copper cathode immersed in copper sulphate solution, and another beaker with a zinc anode immersed in zinc sulphate solution. The two beakers are connected by a salt bridge (a tube filled with potassium nitrate in an agar gel matrix). The zinc is oxidised at the anode, the copper reduced at the cathode, with the overall equation Cu2+ + Zn => Cu + Zn2+, generating an open circuit voltage of 1.1018 Volts.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP15088769
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
DANIELLCELLELECTROCHEMICALELECTROCHEMISTRYBATTERYELECTRICITYELECTRICVOLTVOLTAGEPOTENTIALDIFFERENCEREDUCTIONOXIDATIONCATHODEANODECHEMICALCHEMISTRYCOPPERZINCBEAKERSALTBRIDGEELECTRODEPHYSICSPHYSICALFLOWCURRENTEXPERIMENTCLASSICJOHNDANIELL18361830S19THCENTURYHISTORICALHISTORYSULPHATESCHOOLSCIENCESCIENCEEDUCATION
1830S183619THANODEBATTERYBEAKERBRIDGECATHODECELLCENTURYCHEMICALCHEMISTRYCLASSICCOPPERCURRENTDANIELLDANIELLDIFFERENCEEDUCATIONELECTRICELECTRICITYELECTROCHEMICALELECTROCHEMISTRYELECTRODEEXPERIMENTFLOWHISTORICALHISTORYJOHNOXIDATIONPHYSICALPHYSICSPOTENTIALREDUCTIONSALTSCHOOLSCIENCESCIENCESULPHATEVOLTVOLTAGEZINC
 Loading
Loading