
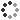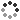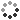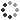
A rooted cutting of a tomato plant, Solanum lycopersicum (formerly Lycopersicon esculentum), made from a side shoot of the main stem. The picture shows the severed end of the cutting (bottom) as it develops new roots. The brown material is fragments of the compost in which the cutting was raised. The new roots appear not from the cut surface, but as outgrowths from the stem just above the cut. This is because root formation is stimulated by the plant hormone auxin, indoleacetic acid (IAA), which is produced by the shoot tip and migrates downwards through the stem. In an intact plant, IAA regulates extension growth, but if the stem is cut, it accumulates above the cut surface, and stimulates the formation of new roots. Cuttings are used in horticulture to propagate a wide variety of plants. For the amateur grower, cuttings are an inexpensive way of gaining new plants.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP15591600
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading