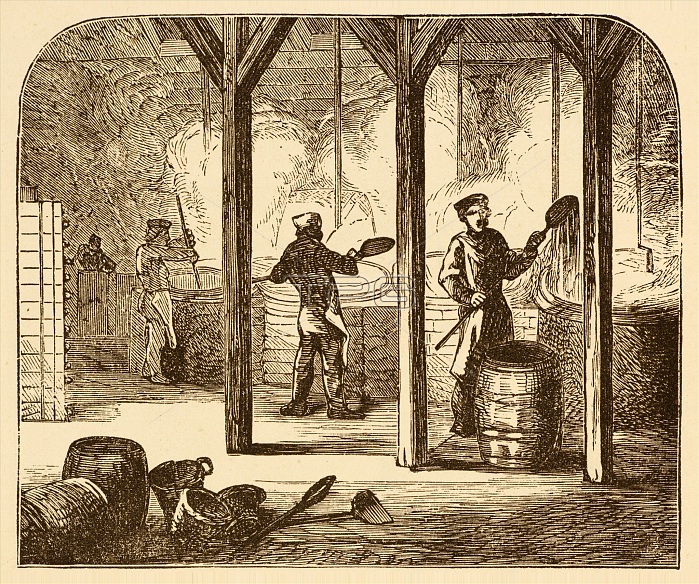

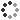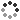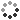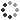
19th century illustration of a soap boiling house. In chemistry, soap is a salt of a fatty acid. Hot-processed soaps are created by encouraging the saponification reaction by adding heat to speed up the reaction. Saponification is a process that produces soap, usually from fats and lye. In contrast with cold-pour soap which is poured into molds and for the most part only then saponifies, hot-process soaping for the most part saponifies the oils completely and only then is poured into molds. In the fully boiled process on an industrial scale, the soap is further purified to remove any excess sodium hydroxide, glycerol, and other impurities, colour compounds, etc. These components are removed by boiling the crude soap curds in water and then precipitating the soap with salt.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP16636364
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading