
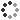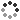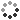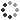
Geodes are roughly spherical objects that form in various geologic environments. One method involves basalts (dark fine grained igneous rocks) typical of lava flows worldwide. Gases dissolved in molten rock (magma) can form bubbles, like the ones we see in carbonated drinks. Rapid cooling of magma traps these bubbles as irregular or rounded cavities, or open spaces, in the basalt. Groundwater may then trickle through the rock and, over time, dissolve silica (silicon oxide) from the rock and re-precipitate the silica in layers on the insides of the cavities. This creates banded agate. A final stage of precipitation may leave a 'druse', or layer of tiny quartz crystals, as a final stage before the water stops flowing. Weathering of the basalt frees these balls of hard silica into the soil, from which they can be collected and split open to reveal the layers inside.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22084577
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading