
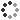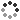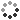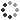
A cryo-electron micrograph showing a single layer of evenly spaced enzyme structures (colorful "wheels") interspersed with gold nanoparticles (magenta). The colorful wheel images are computer-generated models of the molecular structure of the enzyme, superimposed over the electron micrograph where the enzymes are located in the array. Constructing such regular arrays of biomolecules might help develop high efficiency electrodes for biofuels or improve the resolution of cryo-electron microscopy in structural biology. In the field of energy conversion, scientists have been searching for efficient ways to convert organic fuels such as ethanol into electricity using catalytic electrodes. But making single layers of densely packed enzymes, the functional part of such catalytic electrodes, has been a challenge. This new research shows that precisely engineered gold nanoparticles can be used to "glue" enzymes together to form oriented and ordered single layers, and that these monolayers are mechanically stable enough to be transferred onto a solid surface such as an electrode.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22224221
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading