
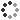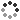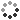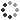
A giant of a moon appears before a giant of a planet undergoing seasonal changes in this natural color view of Titan and Saturn from NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Titan, Saturn's largest moon, measures 3,200 miles, or 5,150 kilometers, across and is larger than the planet Mercury. Cassini scientists have been watching the moon's south pole since a vortex appeared in its atmosphere in 2012. As the seasons have changed in the Saturnian system, and spring has come to the north and autumn to the south, the azure blue in the northern Saturnian hemisphere that greeted Cassini upon its arrival in 2004 is now fading. The southern hemisphere, in its approach to winter, is taking on a bluish hue. This change is likely due to the reduced intensity of ultraviolet light and the haze it produces in the hemisphere approaching winter, and the increasing intensity of ultraviolet light and haze production in the hemisphere approaching summer. (The presence of the ring shadow in the winter hemisphere enhances this effect.) The reduction of haze and the consequent clearing of the atmosphere makes for a bluish hue: the increased opportunity for direct scattering of sunlight by the molecules in the air makes the sky blue, as on Earth. The presence of methane, which generally absorbs in the red part of the spectrum, in a now clearer atmosphere also enhances the blue. This view looks toward the northern, sunlit side of the rings from just above the ring plane.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22312746
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading