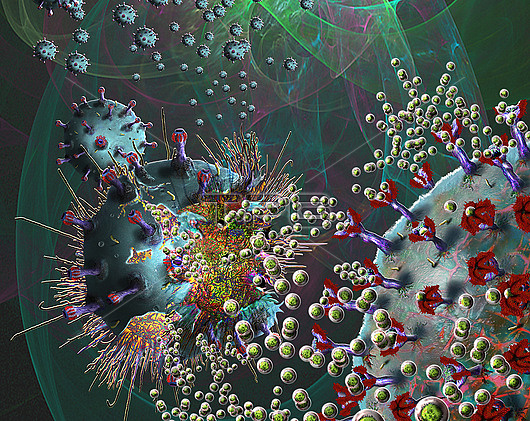
Covid-19 coronavirus vaccine. Illustration of coronavirus particles (blue spheres) being marked by antigens (smaller red spheres at right and lower centre) produced by a potential vaccine. Different strains of coronavirus are responsible for diseases such as the common cold, gastroenteritis and SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome). The new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-CoV) emerged in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The virus causes a mild respiratory illness (Covid-19) that can develop into pneumonia and be fatal in some cases. Vaccines are examples of antigens in an immunogenic form. They prime the immune system to recognise the invading pathogen, with antibodies binding to specific antigens, for instance viral proteins, marking them for destruction by phagocyte immune cells. Research is ongoing into a vaccine for the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, but it is not expected to be available before 2021. This image can also represent immunotherapy by the use of neoantigens (activated proteins from T-cells).
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP25530479
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading