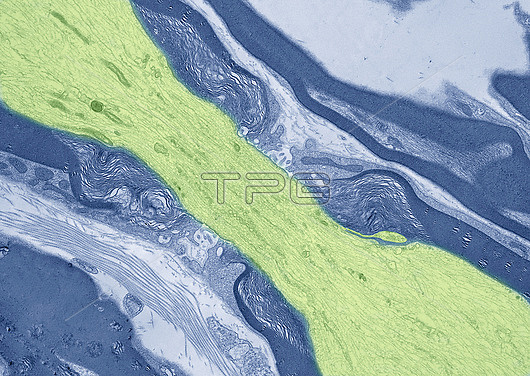
Coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of a longitudinal section through a myelinated nerve fibre. Myelin (dark blue) is an insulating fatty layer that surrounds nerve fibres (axons), increasing the speed at which nerve impulses travel. It is formed when Schwann cells wrap around the fibre, depositing layers of myelin between each coil. At varying intervals along the length of the fibre are gaps, called nodes of Ranvier (centre). Nerve impulses, travelling along the axon as electrical action potentials, jump from node to node in a process known as saltatory conduction.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP26516455
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading