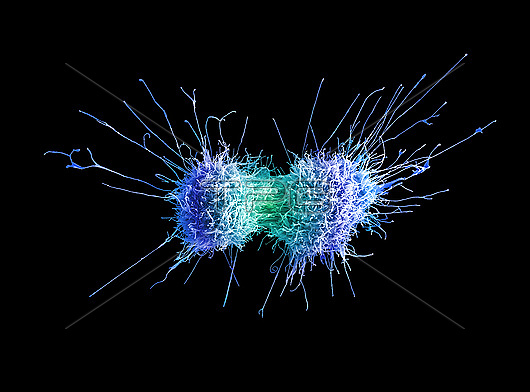
Cervical cancer cell, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). The cervix is the lower part of the womb, also called the neck of the womb, and comprises part of the woman's reproductive system. Cervical cancer is more common in younger women. One of the main causes of cervical cancer is a persistent infection of certain types of human papilloma virus (HPV). In this image the cells are undergoing cytokinesis which is the physical process of cell division which divides the parental cell into two daughter cells. At the end of cytokinesis, the two daughter cells remain connected by the midbody for a short time. Cancer cells often divide and multiply uncontrollably which can lead to the formation of tumours. These cells also have very long extending filopodia like structures. Filopodia contain actin filaments and can have roles in numerous processes including cell-cell interactions, cell migration or as a sensory guide towards a chemoattractant which is a chemical agent that induces a cell to migrate towards it. This may promote tumour growth and the development of metastasis. : x1600 when printed at 10 cm wide.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP28464503
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading