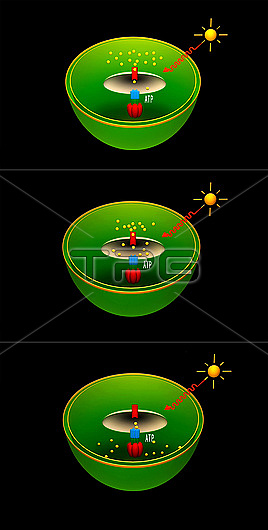
Illustration showcasing the process of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) synthase at work in chloroplasts, which are plant organelles responsible for photosynthesis. ATP synthase is a protein that plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism by providing energy to biological systems. Step 1 (top) shows the accumulation of protons (yellow dots) in the chloroplast stroma (green) during photosynthesis. In Step 2 (middle), the protons move under pressure into the thylakoid lumen (brown oval), which is a membrane-bound compartment inside the chloroplast. In step 3 (bottom), the concentration of these protons rises, and they pass through a specialised channel in ATP synthase, which activates the production of ATP. Through the electron transport chain, an electrochemical gradient is generated, which allows cells to store energy in ATP for later use.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29217888
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
Not Available
Property Release:
Not Available
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading