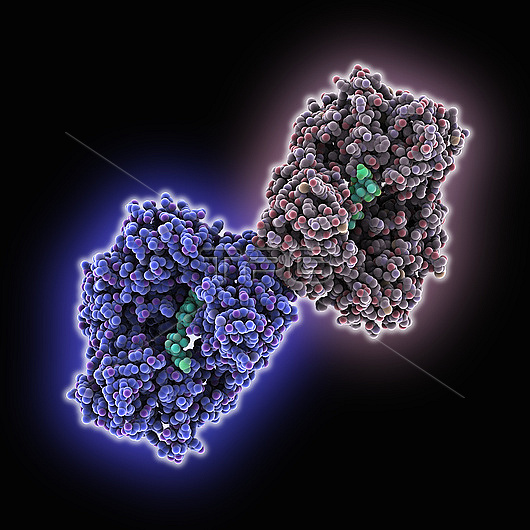
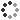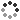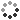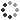
Molecular model of the homo 2-mer human polymerase theta (blue, greyish) complexed with a human ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid, cyan). DNA double-strand breaks often leads to genomic instability and oncogenesis. Their repair mainly occurs through homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining. In homologous-recombination-deficient cells, dna, polymerase, deoxyribonucleic acid, theta becomes critical for double-stranded break repair via microhomology-mediated end joining, also termed theta-mediated end joining. DNA polymerase theta is synthetically lethal with BRCA1/2 and other homologous recombination factors, making it a potential therapeutic target in HR-deficient cancers.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP29943592
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading