
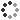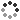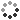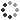
Molecular model of four G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). From left to right the GPCRs are; rhodopsin, which is activated by absorbing light, T-cell receptor, which is activated by a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule presenting an antigen (green), dopamine receptor, which is activated by dopamine (red), and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor B (GABA-B receptor), being activated by the agonist drug baclofen. Activation of the receptors triggers a signalling cascade. In rhodopsin this is occurs when the GPCR's alpha subunit (light blue) activates the phosphodiesterase 6 (purple, bottom left), which breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP, red, bottom left) and leads to sodium channels closing. The other GPCRs activate the enzyme adenylyl cyclase (far centre right), which produces cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, re bottom right). cAMP activates protein kinase C (blue bottom right), which regulates numerous cell functions.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TPG32624959
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RF
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading