
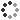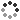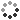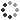
Illustration showing the organic, inorganic and hybrid nanoparticles that can be used to bypass the antibiotic-resistant mechanisms of bacteria (red, centre). Nanomaterials can be used to encapsulate therapeutic agents. They can also be engineered to enter bacterial cells through membrane fusion. Catalytic nanomaterials can increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and causes oxidative cellular stress. Some nanomaterials can bind to various intracellular components, such as DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), ribosomes, etc and disrupt their functions. The bacteria membrane can also be damaged by nanomaterials due to their electrostatic interactions with the bacterial surface.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TPG32699808
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RF
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading