
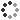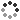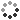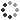
Illustration showing the antibiotic aztreonam (orange) and the drug avibactam (red) bound to bacterial beta lactamase enzymes (blue). Aztreonam usually functions by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which leads to the death of the bacteria. Some bacteria are resistant to aztreonam, however, as they contain beta lactamase. This enzyme hydrolyses (breaks down) a compound in aztreonam called beta lactam, inactivating the drug. Avibactam is a beta lactamase inhibitor, so can prevent this from occurring. Beta lactam antibiotics and beta lactamase inhibitors can be given as a combined treatment where antibiotic resistant bacterial infections are suspected. The molecular structures of aztreonam (top left) and avibactam (top right) are shown with atoms represented as spheres and colour-coded: carbon (grey), hydrogen (white), oxygen (red), hydrogen (blue) and sulphur (yellow).
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TPG35045612
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RF
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading